Script Development Best Practices
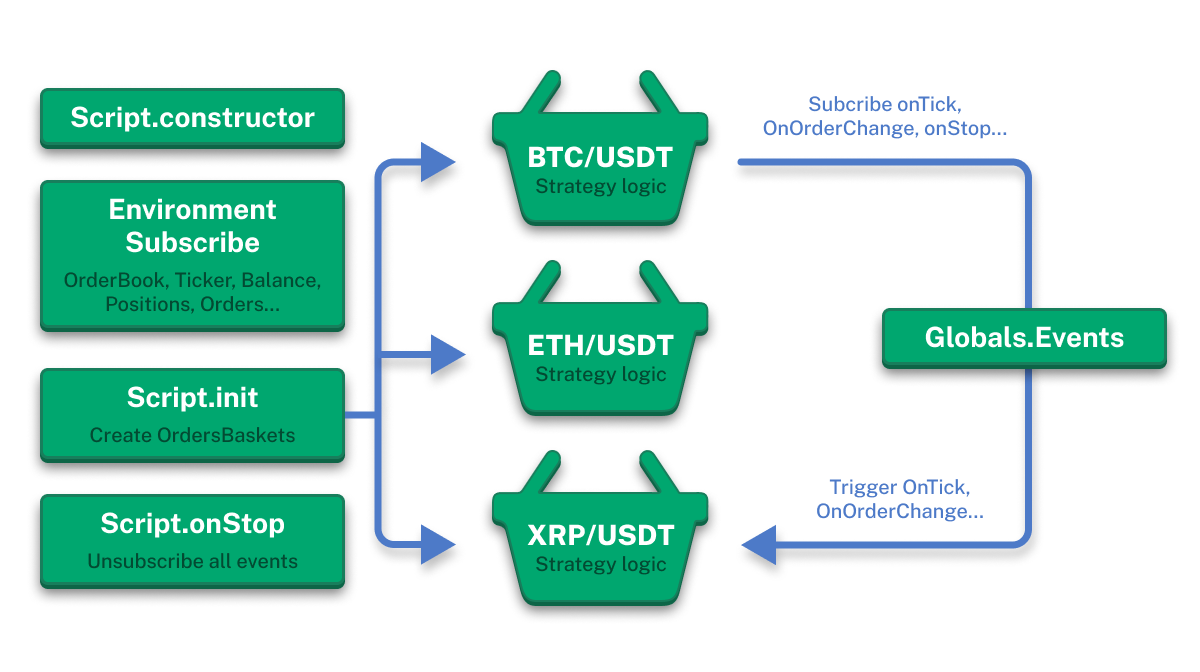
Multi-Currency Trading Bot Architecture
This section describes the key principles for creating effective and reliable trading scripts in JT-Lib, based on separation of responsibilities between the Script and OrdersBasket classes.
Separation of Responsibilities Principle
JT-Lib architecture is built on clear role separation between two main components:
Script Class serves as coordinator and manager:
- Performs overall setup and configuration of trading strategy
- Defines parameters for all trading pairs (symbols)
- Creates and manages
OrdersBasketinstances for each symbol - Monitors and controls all active baskets
- Handles global events and coordinates work between different trading pairs
OrdersBasket Class implements specific trading logic:
- Contains the entire algorithm and trading strategy logic for a specific symbol
- Connects to exchange and manages trading operations for one trading pair
- Handles market data, orders, and positions for its symbol
- Implements specific trading logic (grid, scalping, arbitrage, etc.)
- Works independently from other baskets, ensuring risk isolation
Multi-Currency Architecture
The key advantage of this architecture lies in the ability to create multi-currency trading bots:
-
One Script - Multiple Symbols: Within one script, you can simultaneously trade on multiple trading pairs (BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT, XRP/USDT, etc.)
-
Independent Baskets: Each
OrdersBasketworks with one trading pair independently from others, which means:- Error in one basket doesn't affect others
- Each basket can have its own parameters and settings
- Scalability - adding new trading pairs without changing existing code
-
Centralized Management: Script coordinates work of all baskets through global event system, ensuring:
- Single configuration point
- Centralized reporting and monitoring
- Operation synchronization when needed
Trading Bot Lifecycle
As shown in the diagram above, the lifecycle includes the following stages:
- Script.constructor - initialization of main script class
- Environment Subscribe - subscription to market data (OrderBook, Ticker, Balance, Positions, Orders)
- Script.init - creation of OrdersBasket instances for each symbol
- Script.onStop - proper shutdown and unsubscription from all events
Each stage interacts with all active baskets through the event system, ensuring loose coupling of components and high system reliability.
This section contains recommendations and examples for creating effective and reliable trading scripts in JT-Lib.
Script Parameter Definition
Use the static definedArgs property to define script parameters with default values:
class Script extends BaseScript {
// Define script parameters with default values
static definedArgs = [
{
key: 'symbols',
defaultValue: 'BCH/USDT,BTC/USDT,ADA/USDT,ETH/USDT,XRP/USDT',
},
{
key: 'sizeUsd',
defaultValue: 100,
},
{
key: 'gridStepPercent',
defaultValue: 5,
},
{
key: 'tpPercent',
defaultValue: 2,
},
];
// Script metadata
name = 'Grid Bot Example';
description = 'Multi-coin grid strategy example';
version = 11;
}
Using OrdersBasket for Trading Logic
It's recommended to extract trading logic into separate classes inheriting from OrdersBasket. This ensures modularity and code reusability.
Example: GridBot Strategy
class Script extends BaseScript {
// Define script parameters
static definedArgs = [
{
key: 'symbols',
defaultValue: 'BCH/USDT,BTC/USDT,ADA/USDT,ETH/USDT,XRP/USDT,TRX/USDT,SOL/USDT,LTC/USDT,BNB/USDT,DOGE/USDT',
},
{
key: 'sizeUsd',
defaultValue: 100,
},
{
key: 'gridStepPercent',
defaultValue: 5,
},
{
key: 'tpPercent',
defaultValue: 2,
},
];
// Script metadata
name = 'Grid Bot Example';
description = 'Multi-coin grid strategy example. Strategy logic is based in the GridBasket class.';
version = 11;
// Storage for baskets for each symbol
baskets: Record<string, GridBasket> = {};
private reportLayout: StandardReportLayout;
async onInit() {
// Initialize report
this.reportLayout = new StandardReportLayout();
// Create baskets with delay for connection stability
// This prevents connection issues during initialization
globals.triggers.addTaskByTime({
callback: this.createBaskets,
triggerTime: currentTime() + 60 * 1000, // 1 minute delay
name: 'createBaskets',
});
}
/**
* Create basket for each symbol
* Each basket manages its grid strategy independently
*/
createBaskets = async () => {
for (const symbol of this.symbols) {
// Create new GridBasket instance for each symbol
this.baskets[symbol] = new GridBasket({
symbol,
connectionName: this.connectionName,
});
// Initialize basket (connect to exchange, load position data)
await this.baskets[symbol].init();
}
};
}
/**
* GridBasket - Implements grid trading strategy
*
* Grid strategy works as follows:
* 1. Open long position at market price
* 2. Place limit buy orders below current price at regular intervals
* 3. On price rise - close position with profit
* 4. On price fall - execute limit orders, increase position size
* 5. On price recovery - close larger position with profit
*/
export class GridBasket extends OrdersBasket {
// Strategy parameters
sizeUsd: number = getArgNumber('sizeUsd', 100); // Initial position size in USD
gridStepPercent = getArgNumber('gridStepPercent', 10); // Grid step size in percent
tpPercent = getArgNumber('tpPercent', 2); // Take profit percentage
async init() {
// Initialize parent OrdersBasket
await super.init();
if (this.isInit) {
// If no position, start new trading round
if ((await this.getPositionBySide('long')).contracts === 0) {
await this.newRound();
}
} else {
throw new BaseError('init error - super.init() failed');
}
}
/**
* Start new trading round
* Opens initial long position and sets up grid orders
*/
async newRound() {
// Open initial long position at market price
await this.buyMarket(this.getContractsAmount(this.sizeUsd));
// Create first grid order below current price
await this.createLimitByStep();
}
/**
* Close current round and start new one
* Closes position, cancels all orders and starts over
*/
closeRound = async () => {
// Close long position
await this.closePosition('long');
// Clear all pending limit orders
await this.cancelAllOrders();
// Start new trading round
await this.newRound();
};
/**
* Called on each price tick
* Checks if take profit condition is met
*/
async onTick() {
const position = await this.getPositionBySide('long');
// Check if current price exceeds take profit level
if (position.entryPrice && percentDifference(position.entryPrice, this.close()) > this.tpPercent) {
await this.closeRound();
}
}
/**
* Called on order status change
* Creates new grid orders when limit orders are executed
*/
async onOrderChange(order: Order) {
// When limit buy order is executed (not reduce-only order)
if (order.status === 'closed' && order.reduceOnly === false && order.type === 'limit') {
// Create next grid order at lower price
await this.createLimitByStep();
}
}
/**
* Create limit buy order one grid step below current price
* This order will execute on price fall, increasing position size
*/
async createLimitByStep() {
// Calculate trigger price (grid step below current price)
const triggerPrice = this.close() * (1 - this.gridStepPercent / 100);
// Get current position size
const position = await this.getPositionBySide('long');
const amount = position.contracts;
// Place limit buy order
await this.buyLimit(amount, triggerPrice);
}
}
Key Principles
1. Modular Architecture
Separate logic into different classes:
- Script - for coordination and management
- OrdersBasket - for trading logic of each symbol
2. Initialization Delay
Use triggers with delay for stable exchange connection:
globals.triggers.addTaskByTime({
callback: this.createBaskets,
triggerTime: currentTime() + 60 * 1000, // 1 minute delay
name: 'createBaskets',
});
3. Parameter Definition
Use static definedArgs to configure parameters with default values.
4. Script Metadata
Add name, description, version for script identification.
5. Error Handling
Check isInit before performing operations:
if (this.isInit) {
// Safe operation execution
} else {
throw new BaseError('init error - super.init() failed');
}
6. Basket Independence
Each basket should work independently from others, ensuring scalability and error isolation.
7. Reporting Usage
Initialize StandardReportLayout to display strategy results.
Performance Recommendations
- Minimize API calls - cache data where possible
- Use asynchronous operations - don't block main thread
- Handle errors gracefully - don't let one error stop entire strategy
- Monitor memory - properly manage object lifecycle
Next Steps
- Trading Scripts - In-depth study of BaseScript
- Exchange Orders Basket - Detailed study of OrdersBasket
- Event System - EventEmitter for reactive strategies